HISSAN CENTRAL EXAMINATION 2081 (2025)
Grade: XII Time: 2 hrs
F.M.: 50
COMPUTER SCIENCE (4281 M1)
Candidates are required to give their answers in their own
words as far as practicable.
Multiple Choice Questions.
GROUP A
Writes the best alternative.
[9×1=9]
1.Which database language is used for defining schema structures?
a)DML b)DDL
c)DCL d)TCL
ans: b)DDL
2. Which of the following operations are used to extract
data from a
database?
a)SELECT b)DELETE
c)UPDATE d)INSERT
ans: a)SELECT
3. Which of the following is NOT a valid PHP data type?
a)String b)Float
c)Character d)Boolean
ans: c)Character
4.Which symbol is used for single-line comments in JavaScript?
a)// b)/* */
c)<!-- --> d)**
ans a)//
5.What is the default return type of a function in C if no
return type is
specified?
a)void b)int
c)char d)float
Ans: b)int
6. Which network device is used to connect multiple networks together?
a)Hub b)Switch
c)Router d)Repeater
ans: c)Router
7. What is cloud computing?
a)A type of software b)A
type of hardware
c)The delivery of computing services over the internet d)A programming language
Ans: c)The delivery of computing services over the
internet
8. Which of the following is NOT a principle of OOP?
a)Encapsulation b)Inheritance
c) Compilation d)Polymorphism
Ans: c) Compilation
9.Which of the following SDLC models is also known as the
"linear-
sequential model"?
a)Spiral Model b)Waterfall
Model
c)Agile Model d)V-Model
Ans: b)Waterfall Model
Short Answer
Questions: 15×5-25]
GROUP B
10. What is database? Explain any three advantages of DBMS. [2+3=5]
Ans:-
Database:-
It is a collection of interrelated data . These can be stored in the form of tables. A database can be of any size and varying complexity. A database may be generated and manipulated manually or it may be computerized.
Example:
Customer database consists the fields as cname, cno, and ccity.
DBMS:
The software tool package that helps gatekeeper and manage data storage, access and maintenances. It can be either in personal usage scope (MS Access, SQLite) or enterprise level scope (Oracle, MySQL, MS SQL, etc).
DBMS advantages:-
1. Multiple users:
DBMS allows us to share the data among many users and from different sites. It is done to enter multiple data and for the customers. For a complex database, we assign limited access control for them.
2. Backup:
Backup means storing the data in different location or machines. It is done by users or the computers themselves to recover the data in the case of failure. Like reserving a ticket online, suppose 100 persons have reserved and the suddenly the system became down, Now what to do in this scenario, we need old data and new data both. Hence the administrator recovers the data from backup.
3.Data security:-
Obviously, the data for an organization is crucial. What would happen if a hacker or unauthorized person uses it? Our data could be public and misused by third persons for their own purpose. To avoid that risk we assign specific roles to users. We may filter incoming and outgoing data. For this the DBMS is helpful.
OR
Explain second normal form with example. [5]
Second normal form:-
|
item |
colors |
price |
tax |
|
T-shirt |
Red |
13 |
0.45 |
|
T-shirt |
Blue |
13 |
0.45 |
|
polo |
red |
12 |
0.4 |
|
item |
colors |
|
T-shirt |
Red |
|
T-shirt |
Blue |
|
polo |
red |
|
item |
price |
tax |
|
T-shirt |
13 |
0.45 |
|
T-shirt |
13 |
0.45 |
|
polo |
12 |
0.4 |
11. Write a javascript function that takes two numbers as arguments and returns their sum.[5]
Ans:
<script>
var a,b;
function sum(a,b)
{
return a+b;
}
a=parseInt(prompt("enter a number for a"));
b=parseInt(prompt("enter a number foor b"));
document.write(sum(a,b));
</script>
OR
Write a PHP script to find the largest of three numbers.
Ans:-
<?php
$number1 = 10;
$number2 = 25;
$number3 = 15;
if ($number1 >= $number2 && $number1 >= $number3)
{
$greatest = $number1;
}
elseif ($number2 >= $number1 && $number2 >= $number3)
{
$greatest = $number2;
}
else
{
$greatest = $number3;
}
echo "The greatest number is: " . $greatest;
?>
12. Explain the concept of inheritance in OOP. How does inheritance help in code reusability?[2+3]
Ans:-
Inheritance:-
13 What is e-learning? Write any three advantages of e-learning. [2+3]
Ans:-
e-learning:-
E-LEARNING is a flexible term used to describe a means of teaching through technology such as a network, browser, CDROM or DVD multimedia platforms. In today's world, mostly, we use internet to learn or teach or share the contents. We do not need to be in a fixed location to learn. It is just like learn 'wherever you go'
Advantages:
1. Availability of same course to millions.
2. Boon for Working class.
3. Apprehensive Employers.
It simply defines the project scope, functionalities, constraints, and user expectations clearly, avoiding misunderstandings later in the development process.
The gathered requirements serve as the foundation for the system design, development, and testing phases. Accurate requirements ensure that the system is built as per user needs.
Well-defined requirements help in estimating project cost, time, and resources effectively, reducing the risk of scope creep, rework, and project failure.
Long Answer
Questions: [2x8-16]
GROUP C
15.What is computer network? Explain any three types of
network topologies with their advantages.
[2+6]
Purpose of networking:-
- Networking for communication medium (have communication among people;internal or external)
- Resource sharing (files, printers, hard drives, cd-rom/)
- Higher reliability ( to support a computer by another if that computer is down)
- Higher flexibility( different system can be connected without any problems)
- Scalable (computers and devices can be added with time without changing original network.
Topology:
When we go for networking, we connect some computers in particular layout or design. This design or pattern of connection is called topology.
There are many types;
Bus topology:
A linear bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end (See fig. 1). All nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable.
Fig. 1. Linear Bus topology
Advantages of a Linear Bus Topology
Installation is easy and cheap to connect a computer or peripheral to a linear bus.
Requires less cable length than a star topology.
Star topology:-
A star topology is designed with each node (file server, workstations, and peripherals) connected directly to a central network hub, switch, or concentrator (See fig. 2).
Data on a star network passes through the hub, switch, or concentrator before continuing to its destination. The hub, switch, or concentrator manages and controls all functions of the network.
It also acts as a repeater for the data flow. This configuration is common with twisted pair cable; however, it can also be used with coaxial cable or fiber optic cable.
Fig. 2. Star topology
Advantages of a Star Topology
Easy to install and wire.
No disruptions to the network when connecting or removing devices.
Easy to detect faults and to remove parts.
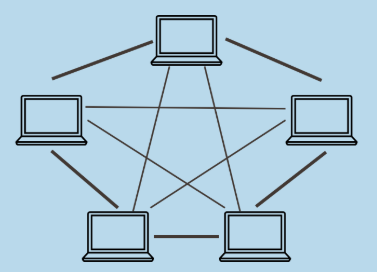
Mesh topology
The mesh topology incorporates a unique network design in which each computer on the network connects to every other, creating a point-to-point connection between every device on the network. The purpose of the mesh design is to provide a high level of redundancy.
It needs/uses n(n-1)/2 channels(paths) and n-1 input/ output ports. If one network cable fails, the data always has an alternative path to get to its destination.- Provides redundant paths between devices
- The network can be expanded without disruption to current users.
16. Write a C program to read and display employee details using a structure. [Define a structure Employee to store employee name (string), ID (integer), and salary (float)]. Write a program to input values for these fields and then display them.
OR
What is pointer? Write a C program to add two numbers using call by reference. [2+6]
Pointer:-
THE END


No comments:
Post a Comment